Abstract
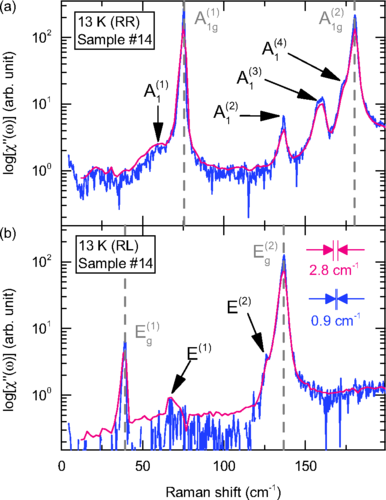
We present a polarization resolved Raman scattering study of surface vibration modes in the topological insulator Bi2Se3 single crystal and thick films. Besides the four Raman active bulk phonons, we observed four additional modes with much weaker intensity and slightly lower energy than the bulk counterparts. Using symmetry analysis, we assigned these additional modes to out-of-plane surface phonons. Comparing with first-principle calculations, we conclude that the appearance of these modes is due to c-axis lattice distortion and van der Waals gap expansion near the crystal surface. Two of the surface modes at 60 and 173 cm(-1) are associated with Raman active A(1g) bulk phonon modes, the other two at 136 and 158 cm(-1) are associated with infrared active bulk phonons with A(2u) symmetry. The latter become Raman allowed due to reduction of crystalline symmetry from D-3d in the bulk to C-3v on the crystal surface. In particular, the 158 cm(-1) surface phonon mode shows a Fano line shape under resonant excitation, suggesting interference in the presence of electron-phonon coupling of the surface excitations.