Abstract
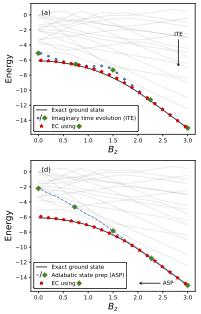
Subspace methods are powerful, noise-resilient methods that can effectively prepare ground states on quantum computers. The challenge is to get a subspace with a small condition number that spans the states of interest using minimal quantum resources. In this work, we will use eigenvector continuation (EC) to build a subspace from the low-lying states of a set of Hamiltonians. The basis vectors are prepared using truncated versions of standard state preparation methods such as imaginary time evolution (ITE), adiabatic state preparation (ASP), and variational quantum eigensolver (VQE). By using these truncated methods combined with eigenvector continuation, we can directly improve upon them, obtaining more accurate ground state energies at a reduced cost. We use several spin systems to demonstrate convergence even when methods like ITE and ASP fail, such as ASP in the presence of level crossings and ITE with vanishing energy gaps. We also showcase the noise resilience of this approach beyond the gains already made by having shallower quantum circuits. Our findings suggest that eigenvector continuation can be used to improve existing state preparation methods in the near term.